Medicines come in a variety of types and formats.
First, let’s look at generic names and brands names.
“What’s the difference?” I hear you cry!
Here’s an example using well known words “vacuum” and “hoover”. Many people don’t realise that hoover is actually a brand name. People think hoover is the generic name but the generic name is actually vacuum. Hoover is the name of a company that did a fantastic job of marketing vacuum cleaners so they are usually referred to as hoovers. Did you know that?
We can put this into context with a medication example using “ibuprofen”. This is a drug that can be bought over the counter without a prescription. You might have used it yourself. Its aim is to reduce hormones that cause inflammation and pain in the body. Ibuprofen is the generic name. There are lots of brand names for ibuprofen. One of the most well known brand names for ibuprofen is Nurofen.
How did you do? Did you spot the difference?
Brand names usually have a capital letter and generic names don’t unless they are at the beginning of a sentence. Not everyone knows this so you can’t always trust what you read.
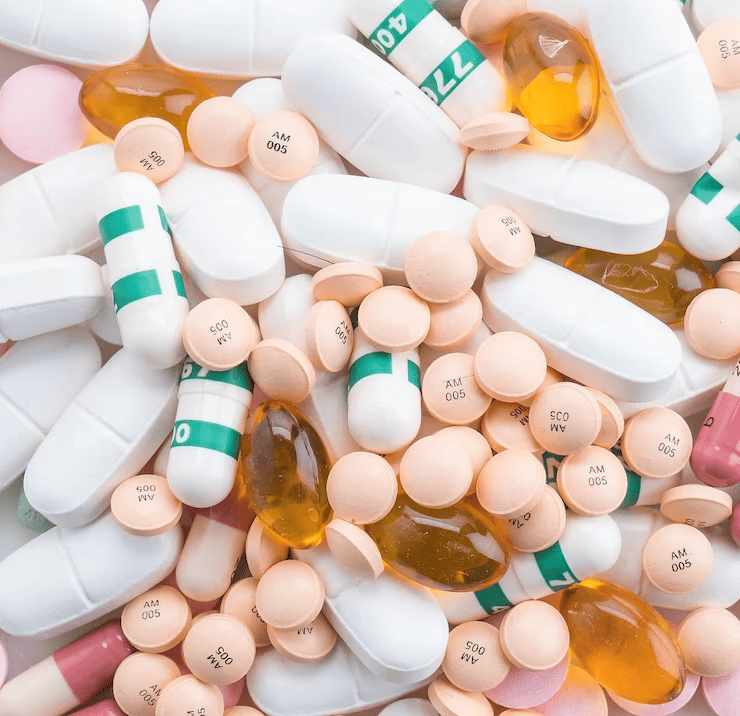
Tablets
Made of compacted powder. Some have a polymer coat to make them smoother and easier to swallow. Tablets may come in a variety of forms, colours and shapes.
- Sugar (enteric) coated protect the stomach from the adverse effects of the medicine. It is absorbed after it has gone through the stomach.
- Slow, modified or controlled release. These are released gradually over a period of time. These should never be crushed or opened.
- Chewable. Used when tablets are too big to swallow.
- Dispersible or soluble. These are easier to take when dissolved in water.
- Sublingual. These are placed under the tongue to dissolve. Here there are lots of blood vessels so that the pain can be relieved quickly, for example, angina pain.
- Buccal. These are placed between the gum and the upper lip so that it will dissolve quickly and be immediately absorbed into the blood stream.
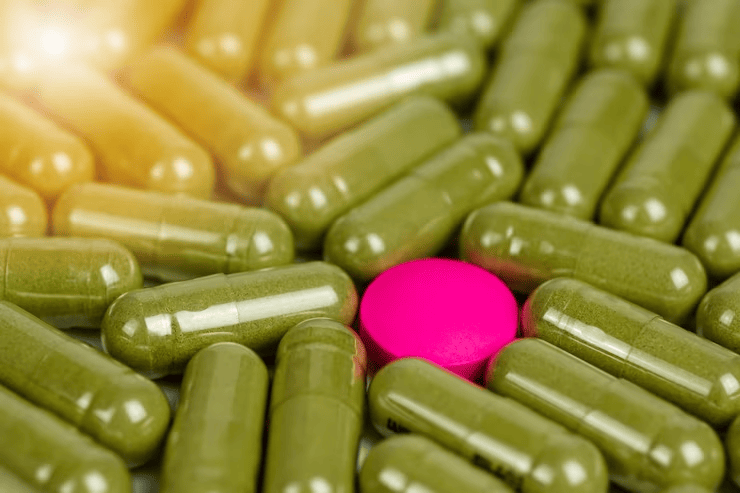

Capsules
- Hard shelled capsules contain powder or mini pellets.
- Soft shelled capsules are made of a gelling agent to contain oils or liquids.
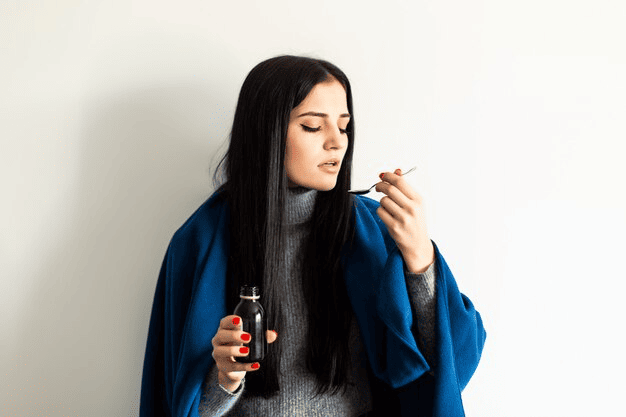

Liquid Medicine
This may be described as:
- an elixir
- a mixture
- a suspension
- a solution
- or a syrup
This will depend on what the active ingredient is mixed with. If an individual finds it difficult to swallow tablets, many oral medications are available in liquids.

Drops and Sprays
These are often used where the active part of the medicine works best if it reaches the affected area directly.
They tend to be used for eyes, ears or nose.
Inhalers and nebulisers
These are inhaled via the mouth and deliver the medication directly to the lungs. Examples are:
- Relievers: Most commonly salbutamol. These open narrowed bronchioles quickly making it easier to breathe.
- Preventers: These contain steroids which reduce inflammation and mucus, and make lungs less sensitive to triggers.
- Protectors: Long-acting reliever drugs and last about 12 hours. These contain steroids which reduce inflammation and mucus, and make lungs less sensitive to triggers.
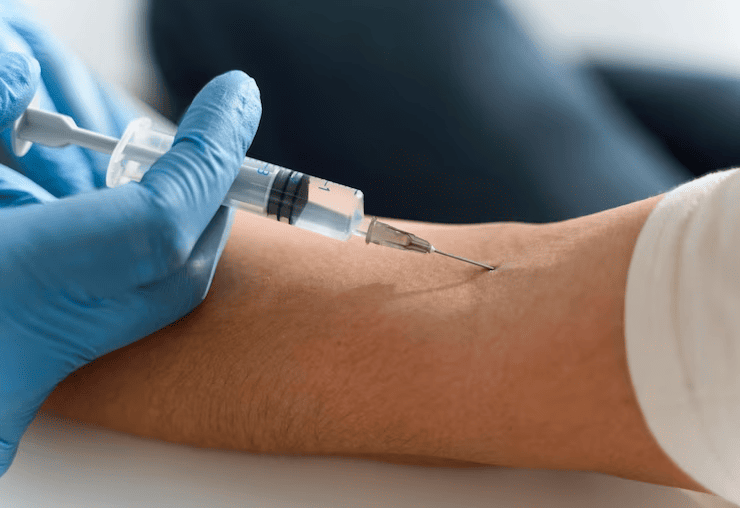
Injections
There are various types of injection, differing in how and where it is injected.
Subcutaneous (SC) injections are given just under the surface of the skin.
Intramuscular (IM) injections are given into a muscle.
Intrathecal injections are given into the fluid around the spinal cord.
Intravenous (IV) injections are given into a vein.
Some injections can be given at home but most are given at a doctor’s surgery (GP) or in hospital.

Patches and implants
Some medicines are absorbed by the body through the skin, such as nicotine patches for help in giving up smoking or contraceptive implants.

Suppositories
The active part of the medicine is combined with another substance and pressed into a ‘bullet shape’ so it can be inserted into the rectum (back passage). Suppositories must not be taken orally by the mouth.
Hopefully these giraffe bottoms will help you to remember this one.

Topical medicines
These are creams, lotions or ointments that are applied directly onto the skin.
They come in tubs, bottles or tubes depending on the type of medicine.