Module 1: Introduction to Angular (1 Hour)
● Introduction to Angular (15 minutes)

○ What is Angular?
■ Angular is a platform for building client-side web applications. It provides tools and libraries to simplify the development process.
■ It is based on components, which are reusable building blocks, making it easier to manage and scale applications.
○ Key features:
■ Components: The fundamental building blocks of Angular applications.
■ Templates: HTML-based views that define the structure of the UI.
■ Data Binding: Automatically synchronizes data between the component and the template.
■ Routing: Enables navigation between different views.
■ Dependency Injection: A design pattern for managing dependencies.
■ TypeScript: A superset of JavaScript that provides static typing.
○ Setting up the development environment:

■ Install Node.js and npm (Node Package Manager).
■ Install the Angular CLI (Command Line Interface) globally.
■ Create a new Angular project.
■ Serve the application.
○ Example:
■ Install Angular CLI: npm install -g @angular/cli
■ Create a new project: ng new my-first-angular-app
■ Navigate to the project: cd my-first-angular-app
■ Run the application: ng serve --open
● Components and Templates (30 minutes)
○ Understanding components:
■ Components are independent, reusable parts of the UI. Each component manages a specific part of the application.

■ A component consists of:
■ A TypeScript class that defines the component's behavior and data.
■ An HTML template that defines the component's view.
■ Metadata (using the @Component decorator) that provides information about the component.
○ Component structure:
■ @Component decorator: Provides metadata, including the selector (how to use the component in a template), the template, and styles.
■ Component class: Contains properties (data) and methods (logic) for the component.
■ Template: The HTML that displays the component's data and defines its structure.
○ Creating and using components:
■ Use the Angular CLI to generate components.
■ Import and use components in other components or modules.
○ Template syntax:
■ Interpolation: Displaying data from the component in the template using {{
}}.
■ Property binding: Setting properties of HTML elements using [ ].
■ Event binding: Responding to user events using ( ).
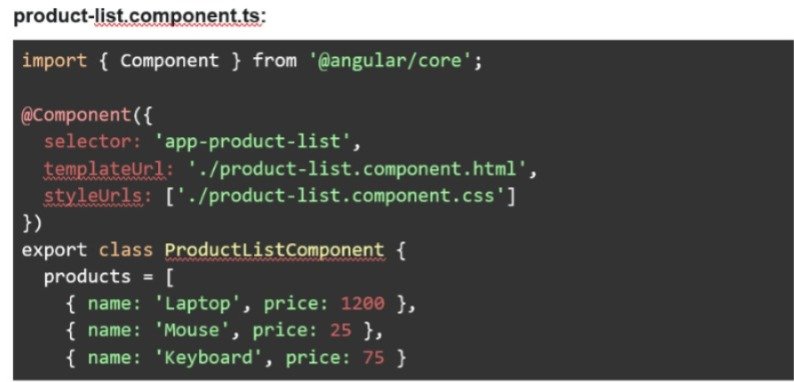
○ Example:
■ Generate a component: ng generate component product-list
.jpeg)
● Data Binding (15 minutes)

○ What is Data Binding?
■ Data binding is a core concept in Angular that allows you to connect the data in your component (TypeScript) to the elements in your template
(HTML). This creates a dynamic and interactive user experience.
○ Types of Data Binding
■ Interpolation: Used to display component data in the template. Data flows from the component to the view.
■ Property Binding: Used to set properties of HTML elements. Data flows from the component to the view.
■ Event Binding: Used to respond to user events (like clicks, input changes).
Data flows from the view to the component.
■ Two-Way Binding: Used to synchronize data between the component and the template. Changes in the view update the component, and changes in the component update the view.
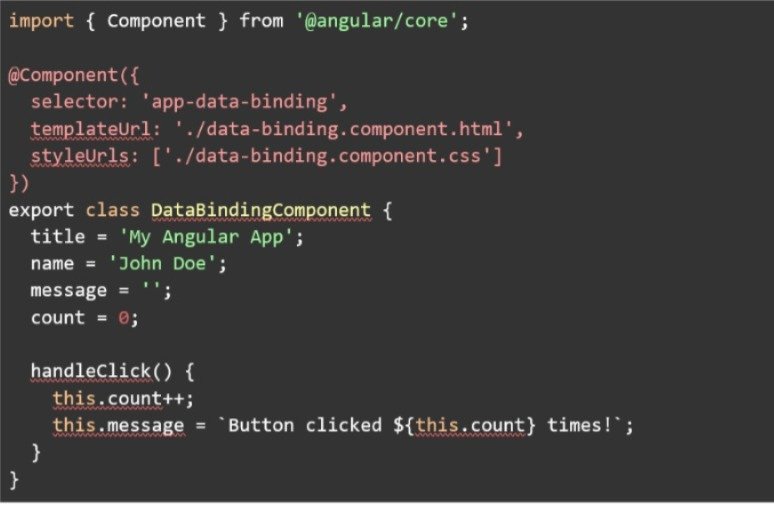
○ Interpolation:
■ Displays data from the component's properties in the template using double curly braces {{ }}.
■ Example: <h1>{{ title }}</h1>
○ Property Binding:
■ Sets the value of an HTML element's property using square brackets [ ].
■ Example: <input type="text" [value]="name">
○ Event Binding:
■ Listens for events (like clicks, input changes) and calls a method in the component. Uses parentheses ( ).
■ Example: <button (click)="handleClick()">Click Me</button>
○ Two-Way Binding:
■ Combines property binding and event binding to keep the component's data and the template's input elements synchronized. Uses [(ngModel)].
Requires importing the FormsModule.
■ Example: <input type="text" [(ngModel)]="myInput"
○ Example:
data-binding.component.ts: